Closure to “Infiltration Model Parameters from Rainfall Simulation for Sandy Soils”
This article is a reply.
VIEW THE ORIGINAL ARTICLEPublication: Journal of Hydrologic Engineering
Volume 29, Issue 5
Get full access to this article
View all available purchase options and get full access to this article.
References
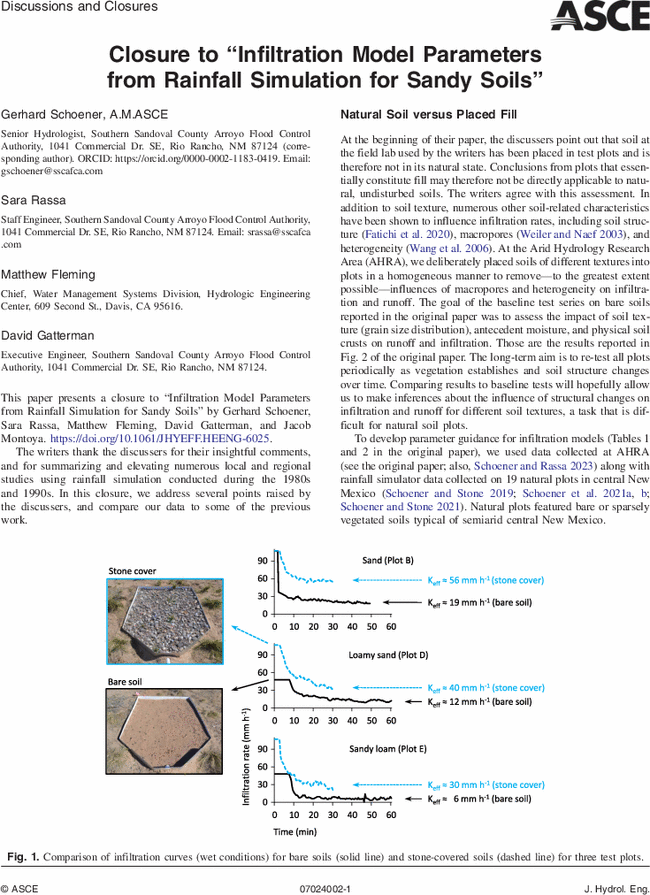
Fatichi, S., D. Or, R. Walko, H. Vereecken, M. H. Young, T. A. Ghezzehei, T. Hengl, S. Kollet, N. Agam, and R. Avissar. 2020. “Soil structure is an important omission in earth system models.” Nat. Commun. 11 (1): 522. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-14411-z.
Gao, H., F. Fenicia, and H. H. Savenije. 2023. “HESS opinions: Are soils overrated in hydrology?” Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 27 (14): 2607–2620. https://doi.org/10.5194/hess-27-2607-2023.
Hardie, M., and A. Almajmaie. 2019. “Measuring and estimating the hydrological properties of a soil crust.” J. Hydrol. 574 (Jul): 12–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.04.031.
Liu, Q., L. Su, C. Zhang, B. Hu, and S. Xiao. 2022. “Dynamic variations of interception loss-infiltration-runoff in three land-use types and their influence on slope stability: An example from the eastern margin of the Tibetan Plateau.” J. Hydrol. 612 (Sep): 128218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2022.128218.
Poesen, J., F. Ingelmo-Sanchez, and H. Mucher. 1990. “The hydrological response of soil surfaces to rainfall as affected by cover and position of rock fragments in the top layer.” Earth Surf. Processes Landforms 15 (7): 653–671. https://doi.org/10.1002/esp.3290150707.
Sabol, G. V., T. J. Ward, and A. D. Seiger. 1982. Rainfall infiltration of selected soils in the Albuquerque drainage area. Las Cruces, NM: Civil Engineering Dept., New Mexico State Univ.
Schoener, G., and S. Rassa. 2023. Arid Hydrology Research Area (AHRA) rainfall simulator data [Dataset]. Davis, CA: Dryad. https://doi.org/10.5061/dryad.kh18932b8.
Schoener, G., and M. C. Stone. 2019. “Impact of antecedent soil moisture on runoff from a semiarid catchment.” J. Hydrol. 569 (Feb): 627–636. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2018.12.025.
Schoener, G., and M. C. Stone. 2021. Data from: Impact of antecedent soil moisture on runoff from a semiarid catchment [Dataset]. Davis, CA: Dryad. https://doi.org/10.5061/dryad.vhhmgqnv1.
Schoener, G., M. C. Stone, and C. Thomas. 2021a. “Comparison of seven simple loss models for runoff prediction at the plot, hillslope and catchment scale in the semiarid southwestern U.S.” J. Hydrol. 598 (Jul): 126490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2021.126490.
Schoener, G., M. C. Stone, and C. Thomas. 2021b. Data from: Comparison of seven simple loss models for runoff prediction at the plot, hillslope and catchment scale in the semiarid southwestern U.S. [Dataset]. Davis, CA: Dryad. https://doi.org/10.5061/dryad.tb2rbp01j.
Wang, K., R. Zhang, and H. Yasuda. 2006. “Characterizing heterogeneity of soil water flow by dye infiltration experiments.” J. Hydrol. 328 (3–4): 559–571. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhydrol.2006.01.001.
Ward, T. J. 1986. A study of runoff and erosion processes using large and small area rainfall simulators. Las Cruces, NM: New Mexico Water Resources Research Institute, New Mexico State Univ.
Ward, T. J. 1993. Rainfall 153 simulation to estimate potential sediment loadings to the Albuquerque north diversion channel. Las Cruces, NM: New Mexico Water Resources Research Institute, New Mexico State Univ.
Ward, T. J., and S. B. Bolin. 1989a. Determination of hydrologic parameters for selected soils in Arizona and New Mexico utilizing rainfall simulation. Las Cruces, NM: New Mexico Water Resources Research Institute, New Mexico State Univ.
Ward, T. J., and S. B. Bolin. 1989b. A study of rainfall simulators, runoff and erosion processes, and nutrient yields on selected sites in Arizona and New Mexico. Las Cruces, NM: New Mexico Water Resources Research Institute, New Mexico State Univ.
Ward, T. J., and S. M. Bolton. 1991. Hydrologic parameters for selected soils in Arizona and New Mexico as determined by rainfall simulation. Las Cruces, NM: New Mexico Water Resources Research Institute, New Mexico State Univ.
Weiler, M., and F. Naef. 2003. “An experimental tracer study of the role of macropores in infiltration in grassland soils.” Hydrol. Process. 17 (2): 477–493. https://doi.org/10.1002/hyp.1136.
Information & Authors
Information
Published In
Copyright
© 2024 American Society of Civil Engineers.
History
Received: Apr 15, 2024
Accepted: May 14, 2024
Published online: Aug 2, 2024
Published in print: Oct 1, 2024
Discussion open until: Jan 2, 2025
Authors
Metrics & Citations
Metrics
Citations
Download citation
If you have the appropriate software installed, you can download article citation data to the citation manager of your choice. Simply select your manager software from the list below and click Download.
